Space Weather Alert - 30th August 2019
What Has Happened?
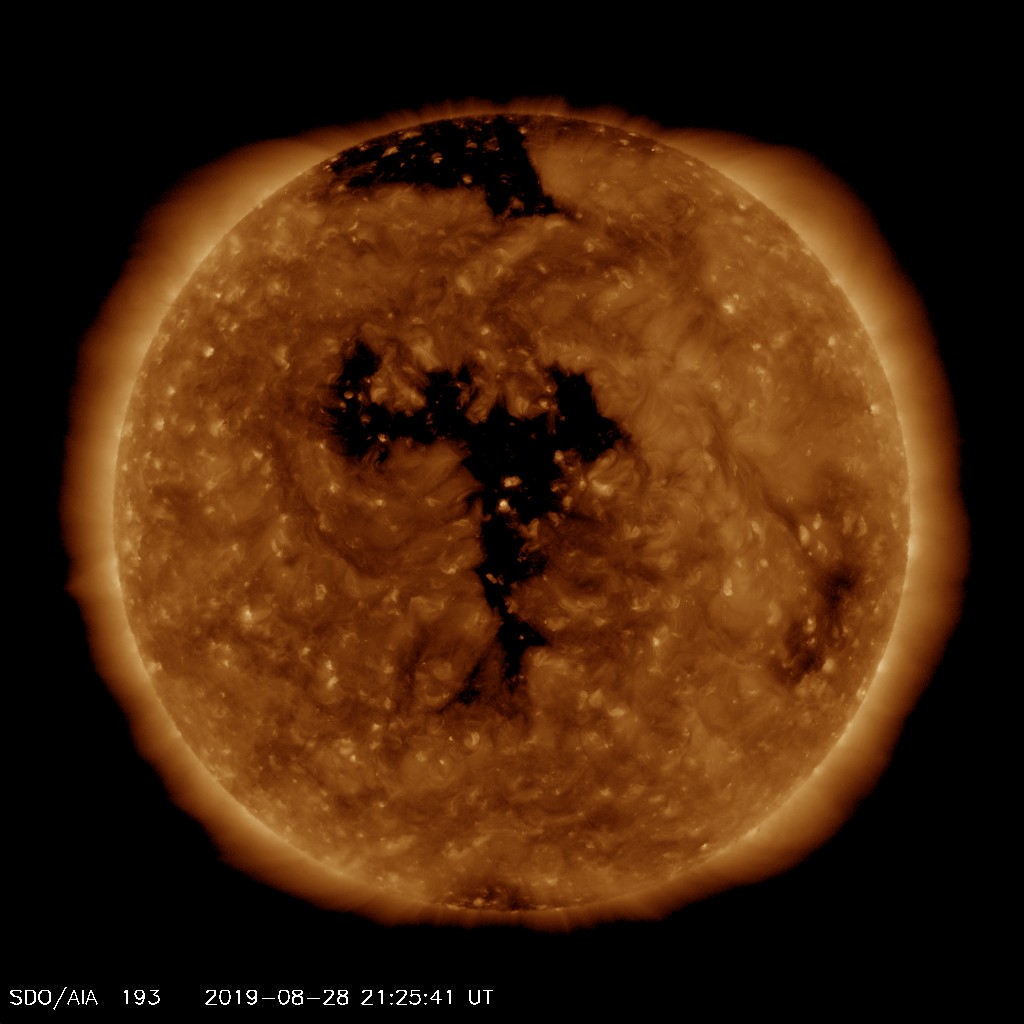
A high speed solar wind stream from a large, recurrent, trans-equatorial, coronal hole is anticipated to arrive tomorrow on the 31st August. On previous rotations this coronal hole caused peaks of STORM G1 geomagnetic conditions (see NOAA space weather scales for more details about these storm levels). This time it has been Earth-facing from the 28th - 30th August.
Geomagnetic activity is likely to reach a maximum of STORM G2 tomorrow as we are closer to the autumn equinox and the coronal hole has grown in size. Some peak activity is likely to occur with the initial arrival of the high speed stream with the elevated solar wind likely to remain geo-effective for 24-48 hours before subsiding.
With some clear dark skies forecast, there is an increased chance of seeing the aurora on Saturday evening into the night. Those in Scotland, northern England and Northern Ireland may have the best chance, if the weather were to be favourable and if geomagnetic activity levels are as expected.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- BGS
- The British Geological Survey is one of the Natural Environment Research Council's Research Centres.
- CME or Coronal Mass Ejection
- The eruption of a portion of the outer atmosphere of the Sun into space, caused by rapid changes in its magnetic field. Often occurs along with a solar flare.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- High Speed Stream
- A fast moving stream of solar wind, responsible for magnetic storms.
- Solar Flare
- Energy released by the explosive reorganisation of magnetic fields within the Sun's atmosphere.
- Magnetogram
- The variation, minute by minute, of the strength and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. Measured in units of nano-Tesla (for the strength of the field) or in degrees (direction of the field).
- Solar Wind
- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.
- Sunspot/Active Region
- A region of intense magnetic field in the Sun's visible outer atmosphere often associated with flares and CMEs.